Nutrition Gut Health Series: The Difference Between Probiotics and Prebiotics
Nutrition Gut Health Series: The Difference Between Probiotics and Prebiotics
What are Probiotics?
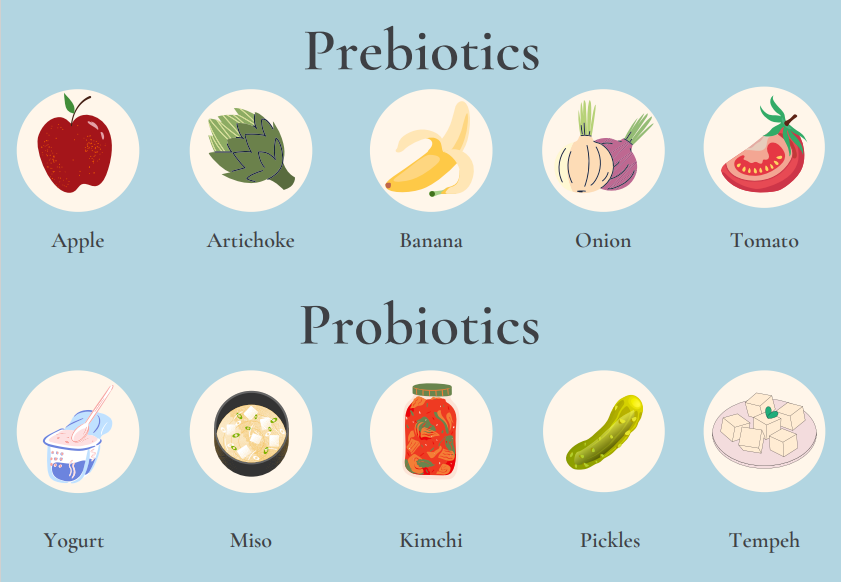
Probiotics are bacteria that are found in certain foods and supplements. Fermented foods such as yogurt, kombucha, sauerkraut, kimchi, miso, tempeh, and kefir contain naturally occurring bacteria. Probiotic supplements are pills containing live bacteria and vary based on bacterial species and concentration. Common types of probiotic supplements include Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus. You may see the term CFU used on supplements, which stands for colony forming units and refers to the number of live organisms contained in the supplement.
What are Prebiotics?
Prebiotics are fermentable fibers found in certain foods that are indigestible to humans. These fibers are fermented by the bacteria living in your gut, also known as the microbiome. Prebiotics benefit the growth of the healthy bacteria living in your gut. Prebiotics are found in many different fruits, vegetables, and whole grains including apples, artichokes, bananas, barley, garlic, green vegetables, oats, onions, tomatoes, and wheat.
What are the benefits of Probiotics and Prebiotics?
If you have ever been put on an antibiotic, your doctor may have recommended that you consume yogurt while on the medication. This is because antibiotics can affect the bacteria living in your gut causing beneficial bacteria to die off, leading to an imbalance of bacteria within your gut. Consumption of foods containing probiotics, such as yogurt, during the course of antibiotic treatment has been shown to preserve the composition of bacteria in the gut and reduce the risk of diarrhea.
With regards to probiotic supplementation, there are many different types of probiotics on the market all with varying concentrations. While some studies have shown benefits of probiotic supplementation for patients with irritable bowel syndrome, it is best to speak with a Registered Dietitian before adding a supplement into your daily routine.
Although prebiotic supplements are available on the market it is recommended to consume prebiotics from a variety of whole food sources as these contain important vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that are missing from the supplements. Not only do prebiotics benefit healthy bacteria living in your gut, but they also help the body absorb calcium, aid in constipation, and blood sugar control. As prebiotics are fibers, it is important to note that eating too much can lead to gastrointestinal symptoms including gas and bloating. It is best to start with small amounts and work up from there.
If you are struggling with gastrointestinal issues, reach out to a Registered Dietitian to receive advice and guidance on adding food sources of prebiotics and probiotics into your diet!


 Home Base
Home Base